介绍
插入式排序属于内部排序法,是对于欲排序的元素以插入的方式找寻该元素的适当位置,以达到排序的目的。
思想
插入排序(Insertion Sorting)的基本思想是:把n个待排序的元素看成为一个有序表和一个无序表,开始时有序表中只包含一个元素,无序表中包含有n-1个元素,排序过程中每次从无序表中取出第一个元素,把它的排序码依次与有序表元素的排序码进行比较,将它插入到有序表中的适当位置,使之成为新的有序表。
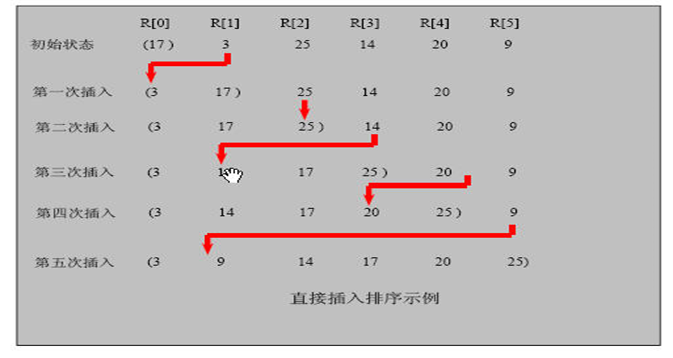
逐步推导法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| import java.util.Arrays;
public class InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {101, 34, 119, 1};
insertSort(arr);
}
public static void insertSort(int[] arr) {
int insertVal = arr[1];
int insertIndex = 1 - 1;
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < arr[insertIndex]) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
arr[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
System.out.println("第1轮插入");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
insertVal = arr[2];
insertIndex = 2 - 1;
while(insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < arr[insertIndex] ) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
arr[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
System.out.println("第2轮插入");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
insertVal = arr[3];
insertIndex = 3 - 1;
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < arr[insertIndex]) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
arr[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
System.out.println("第3轮插入");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import java.util.Arrays;
public class InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {101, 34, 119, 1};
insertSort(arr);
}
public static void insertSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int insertVal = arr[i];
int insertIndex = i - 1;
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < arr[insertIndex]) {
arr[insertIndex + 1] = arr[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
arr[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
System.out.println("第" + i + "轮插入");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
|
